Click here and press the right key for the next slide (or swipe left)
also ...
Press the left key to go backwards (or swipe right)
Press n to toggle whether notes are shown (or add '?notes' to the url before the #)
Press m or double tap to slide thumbnails (menu)
Press ? at any time to show the keyboard shortcuts

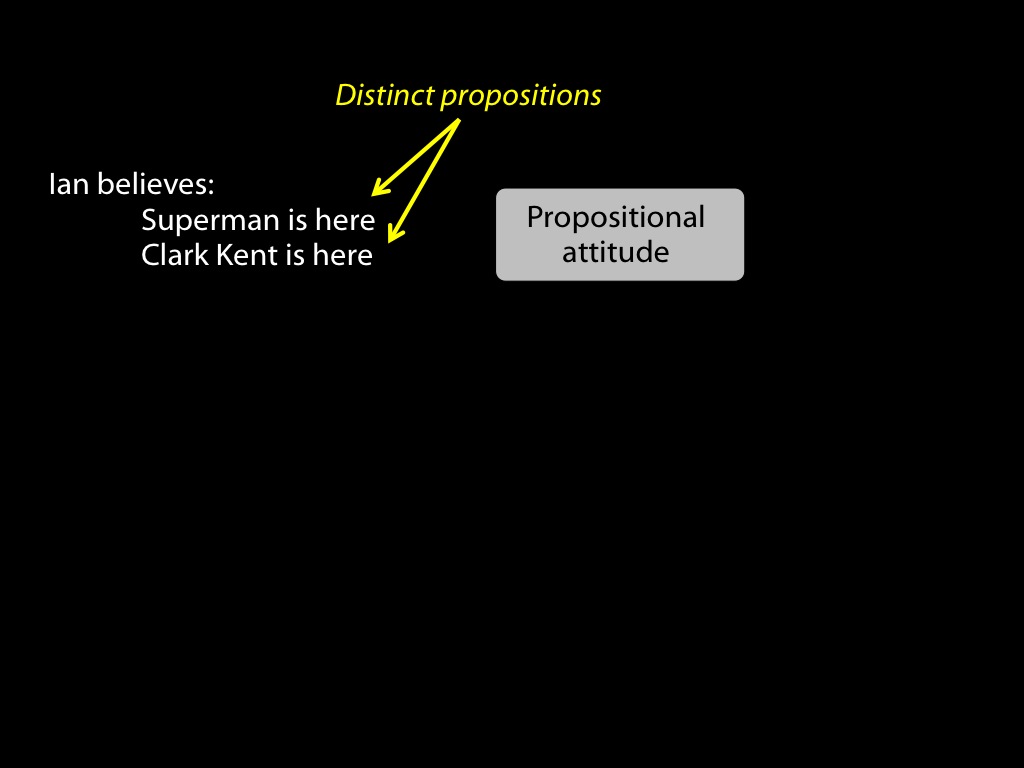
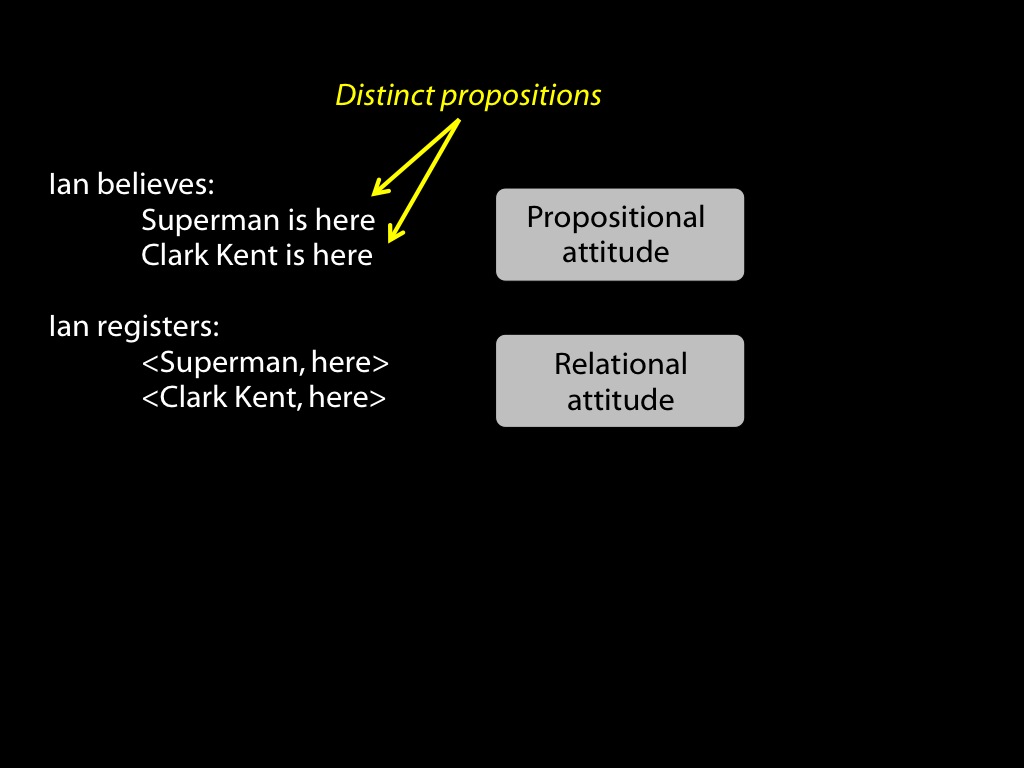
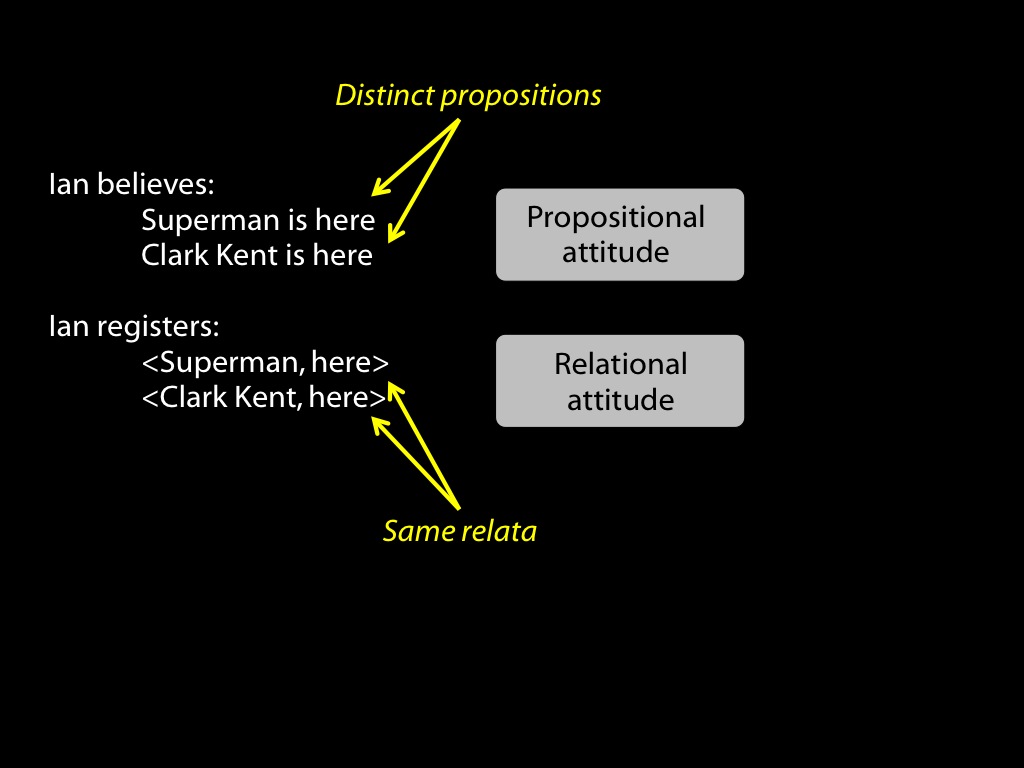
abilities to track mental states are widespread among animals
tracking vs representing mental states
What is observed: that nonhumans track others’ mental states.
Tracking mental states does not require representing them.
So:
How can we draw conclusions about what nonhumans represent?
‘we should be focused not on the yes–no question (do chimpanzees have a theory of mind?), but rather on a whole panoply of more nuanced questions concerning precisely what chimpanzees do and do not know about the psychological functioning of others’
Hare et al (2001, 149)
What models of minds and actions, and of behaviours,
and what kinds of processes,
underpin mental state tracking in different animals?
Way forward:
1. Construct a theory of behaviour reading
2. Construct a theory of mindreading

What models of minds and actions underpin mental state tracking in chimpanzees, scrub jays and other animals?
Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind?
Could a system characterised by minimal theory of mind explain chimpanzee theory of mind abilities?
- yes
But does it?

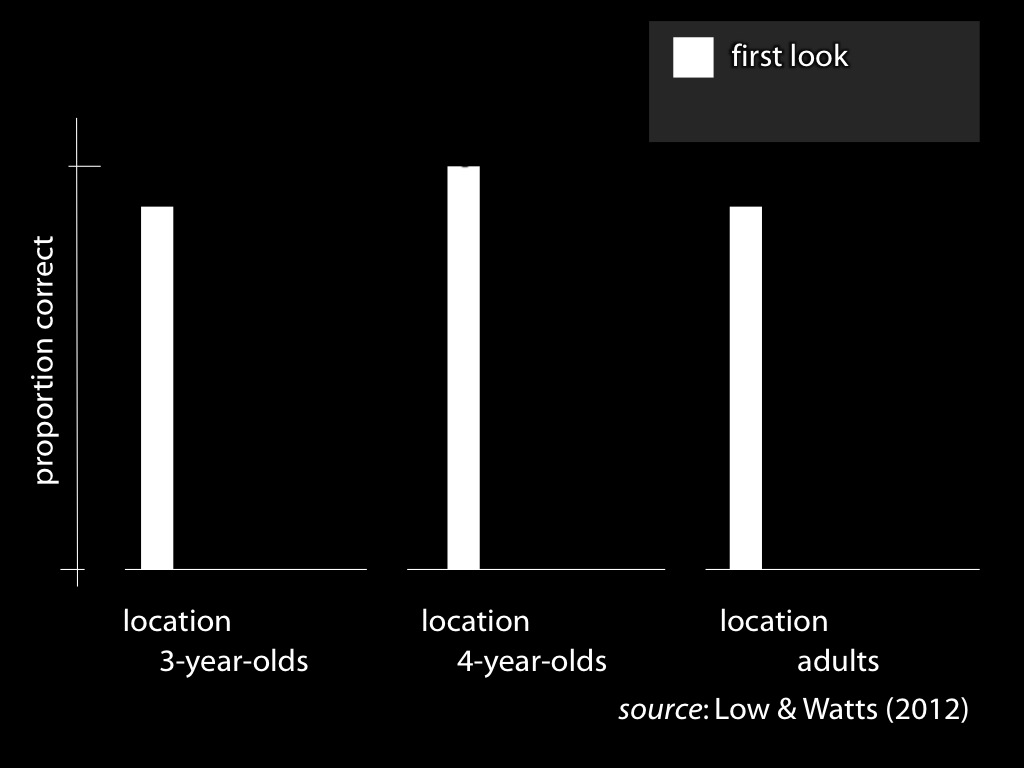
Signature Limits (Part I)

signature limits generate predictions
Hypothesis:
Some belief-tracking in chimpanzees (say) relies on minimal models of the mental.
Hypothesis:
Human infants’ belief-tracking abilities rely on minimal models of the mental.
Prediction:
Some chimpanzee belief-tracking is subject to the signature limits of minimal models.
Prediction:
Infants’ belief-tracking is subject to the signature limits of minimal models.
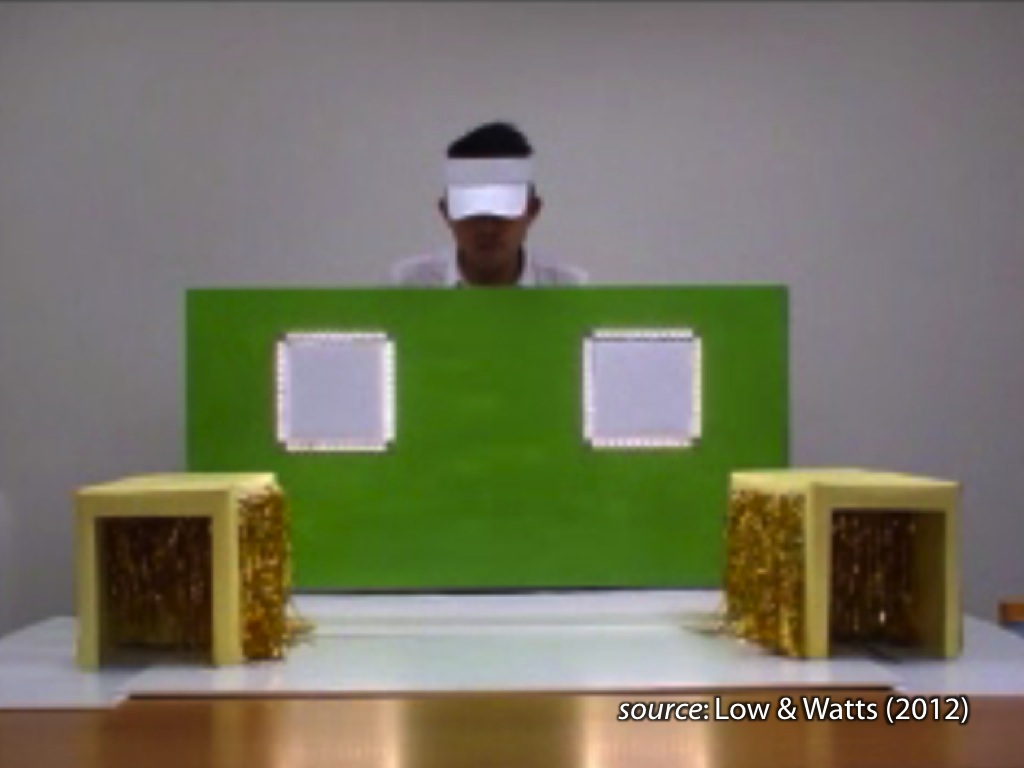
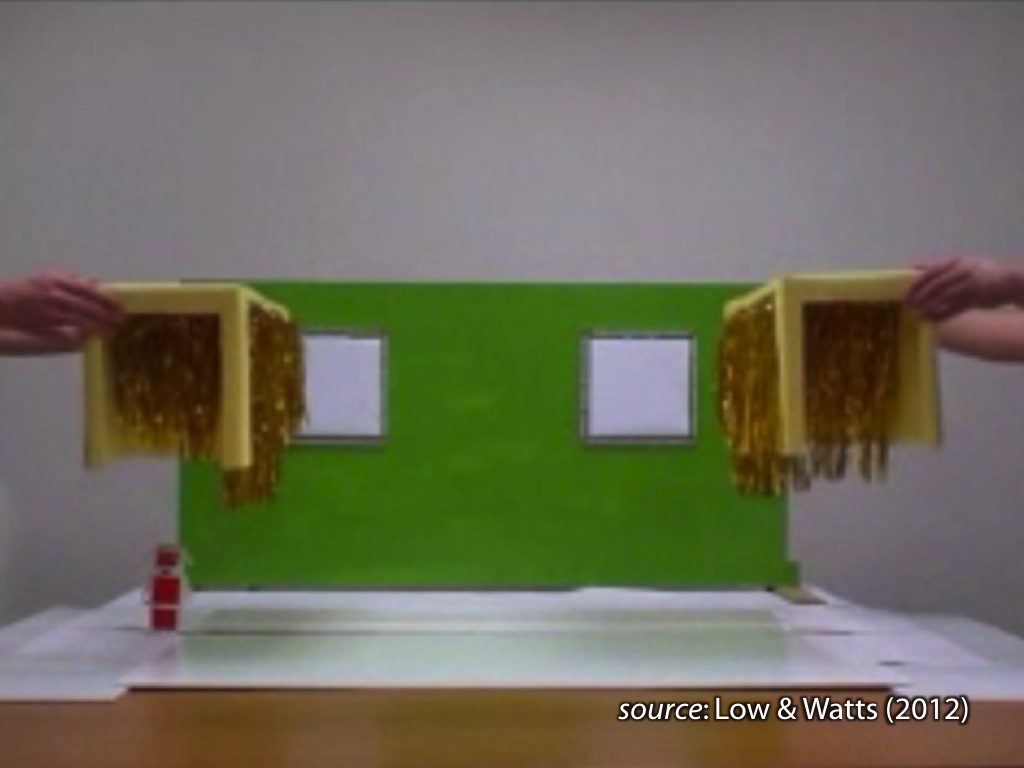
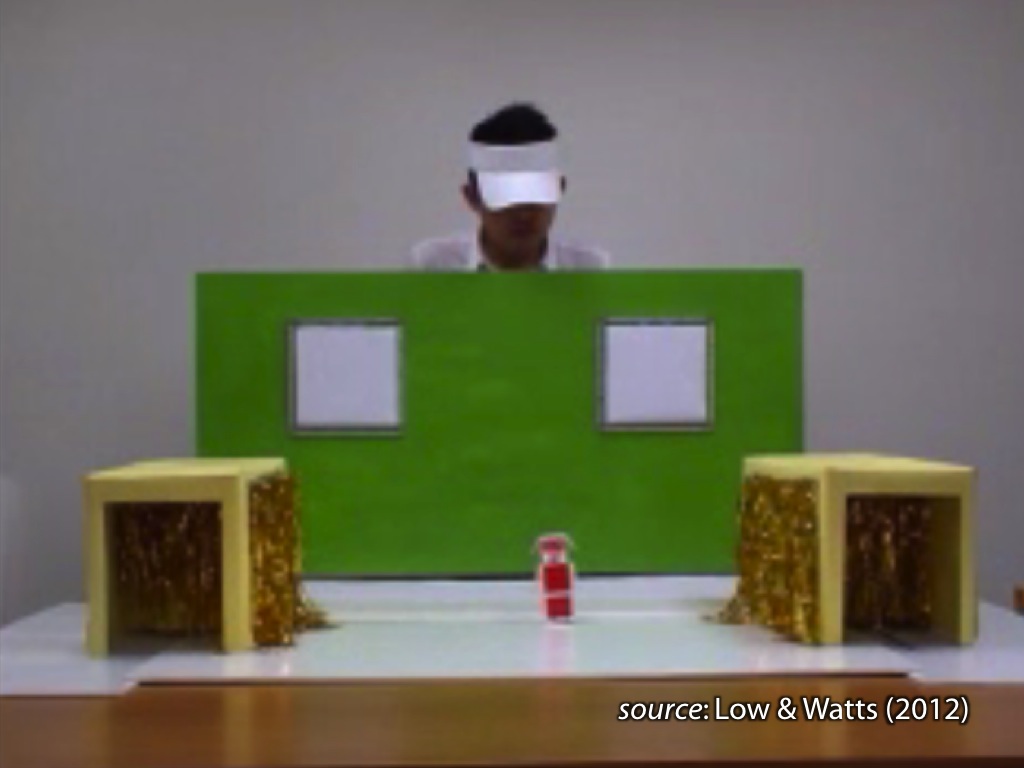
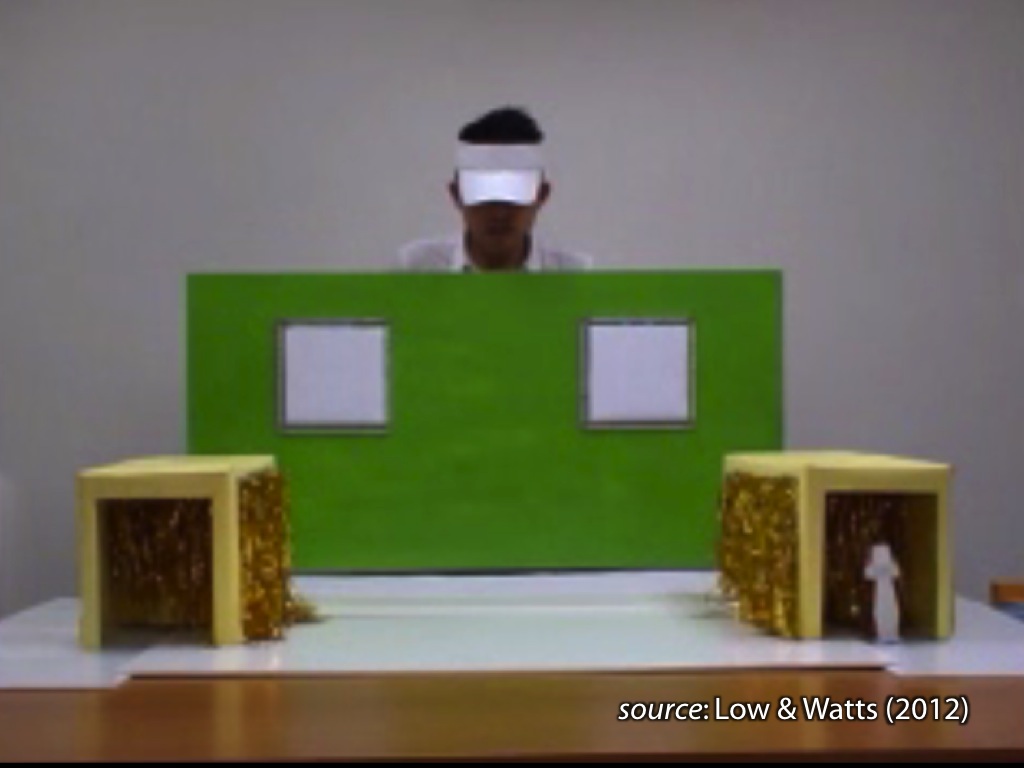
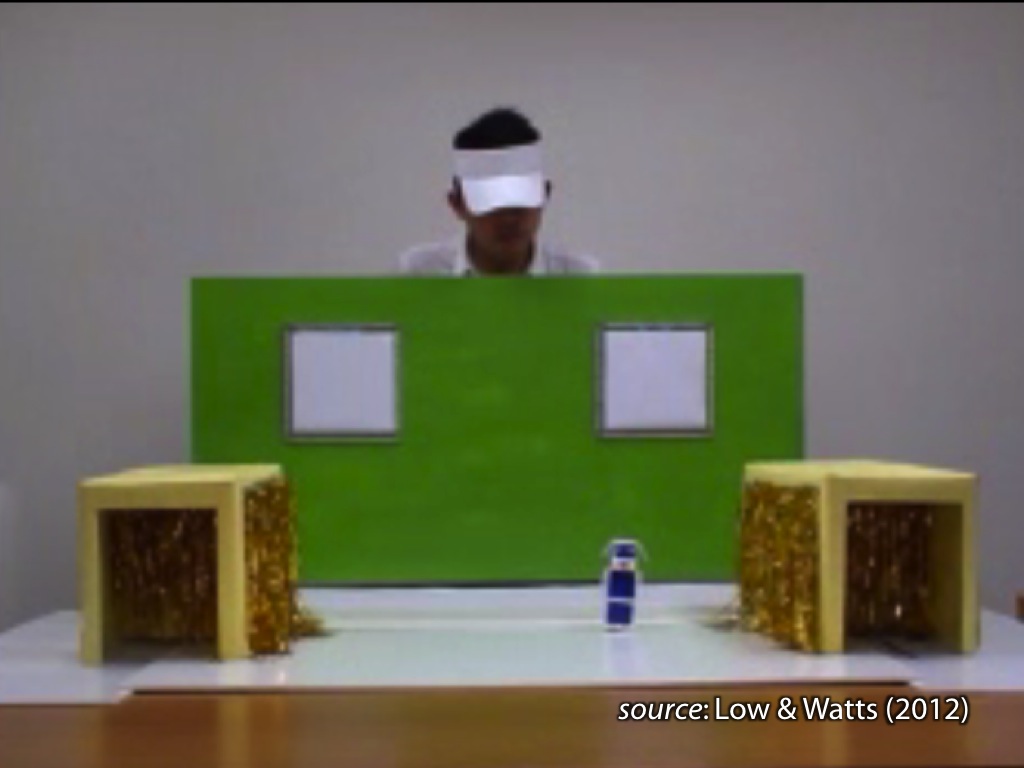
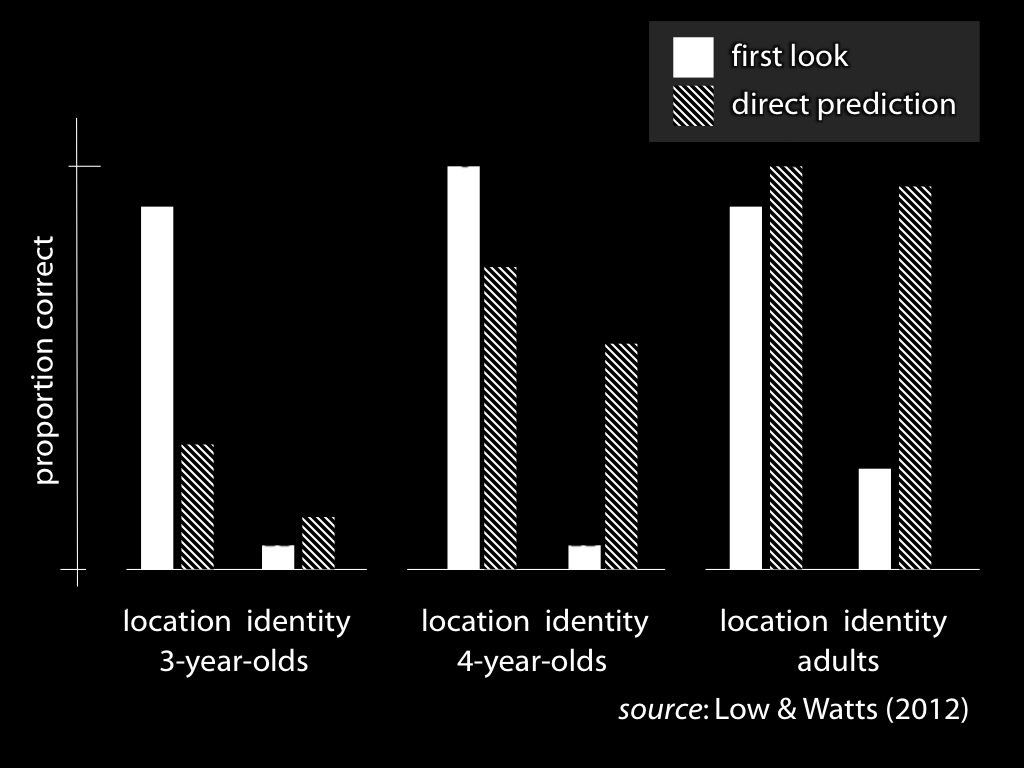
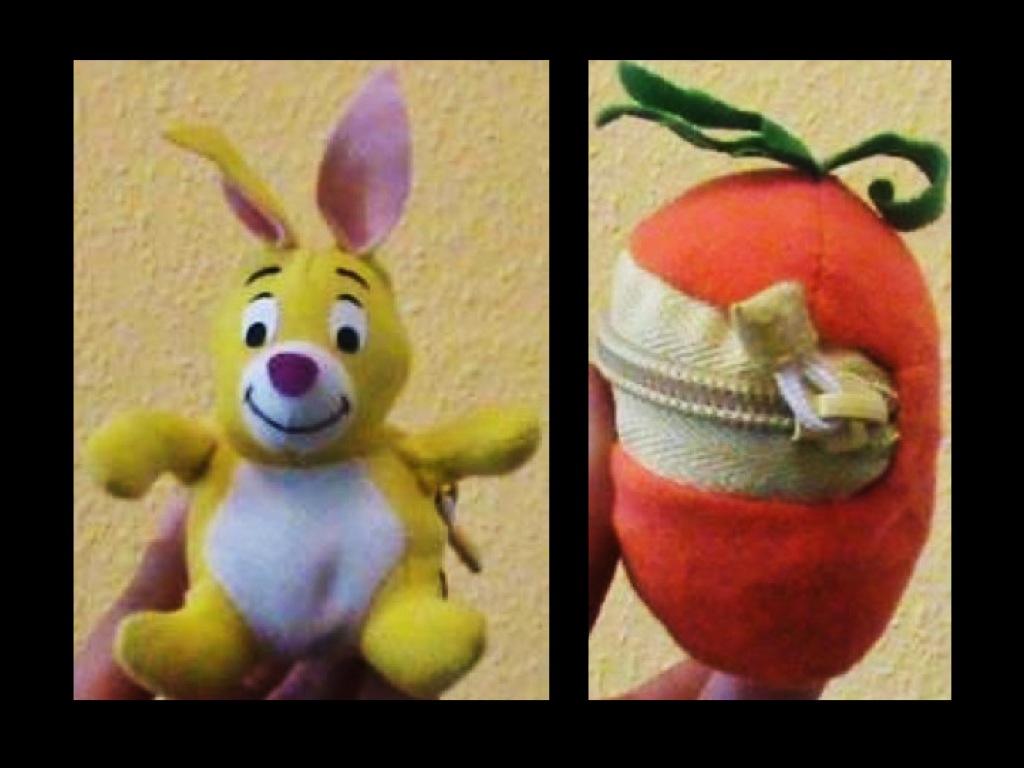








signature limits generate predictions
Hypothesis:
Some belief-tracking in chimpanzees (say) relies on minimal models of the mental.
Hypothesis:
Human infants’ belief-tracking abilities rely on minimal models of the mental.
Prediction:
Some chimpanzee belief-tracking is subject to the signature limits of minimal models.
Prediction:
Infants’ belief-tracking is subject to the signature limits of minimal models.
reidentifying systems:
same signature limit -> same system
What models of minds and actions underpin mental state tracking in chimpanzees, scrub jays and other animals?
Does the chimpanzee have a theory of mind?
Could a system characterised by minimal theory of mind explain chimpanzee theory of mind abilities?
- yes
But does it?
What models of minds and actions, and of behaviours,
and what kinds of processes,
underpin mental state tracking in different animals?
Way forward:
1. Construct a theory of behaviour reading
2. Construct a theory of mindreading

The Teleological Stance
What makes behaviour intelligible to others?
Krupenye et al, 2016
Krupenye et al, 2016
Could behaviour reading be
simply a matter of tracking
joint displacements,
bodily configurations,
and their sensory effects?
We can identify actions from these simuli
without ascribing any mental states
in such a way as to enable us to make useful predictions.
This depends on categorising actions
in ways that abstract from joint displacements,
bodily configurations and their sensory effects.
Dennett : intentional stance / design stance
What makes behaviour intelligible to others?
Criterion of intelligibility ...goals

goal != intention
What is the relation between a purposive action and the outcome or outcomes to which it is directed?


goal != mental state
pure goal ascription
Infer The Goals from The Evidence
The Goals: facts which goals particular actions are directed to...
The Evidence: facts about events and states of affairs that could be known without knowing which goals any particular actions are directed to, nor any facts about particular mental states ...
‘an action can be explained by a goal state if, and only if, it is seen as the most justifiable action towards that goal state that is available within the constraints of reality’
Csibra & Gergely (1998, 255)
1. action a is directed to some goal;
2. actions of a’s type are normally means of realising outcomes of G’s type;
3. no available alternative action is a significantly better* means of realising outcome G;
4. the occurrence of outcome G is desirable;
5. there is no other outcome, G′, the occurrence of which would be at least comparably desirable and where (2) and (3) both hold of G′ and a
Therefore:
6. G is a goal to which action a is directed.
pure goal ascription = no mental state ascriptions needed
Davidson & Dennett
from:
joint displacements, bodily configurations and their effects
to:
propositional attitudes (belief, desire, ...)
Csibra & Gergely
from:
joint displacements, bodily configurations and their effects
to:
goal-directed actions
to:
propositional attitudes (belief, desire, ...)
What models of minds and actions, and of behaviours,
and what kinds of processes,
underpin mental state tracking in different animals?
Way forward:
1. Construct a theory of behaviour reading
2. Construct a theory of mindreading
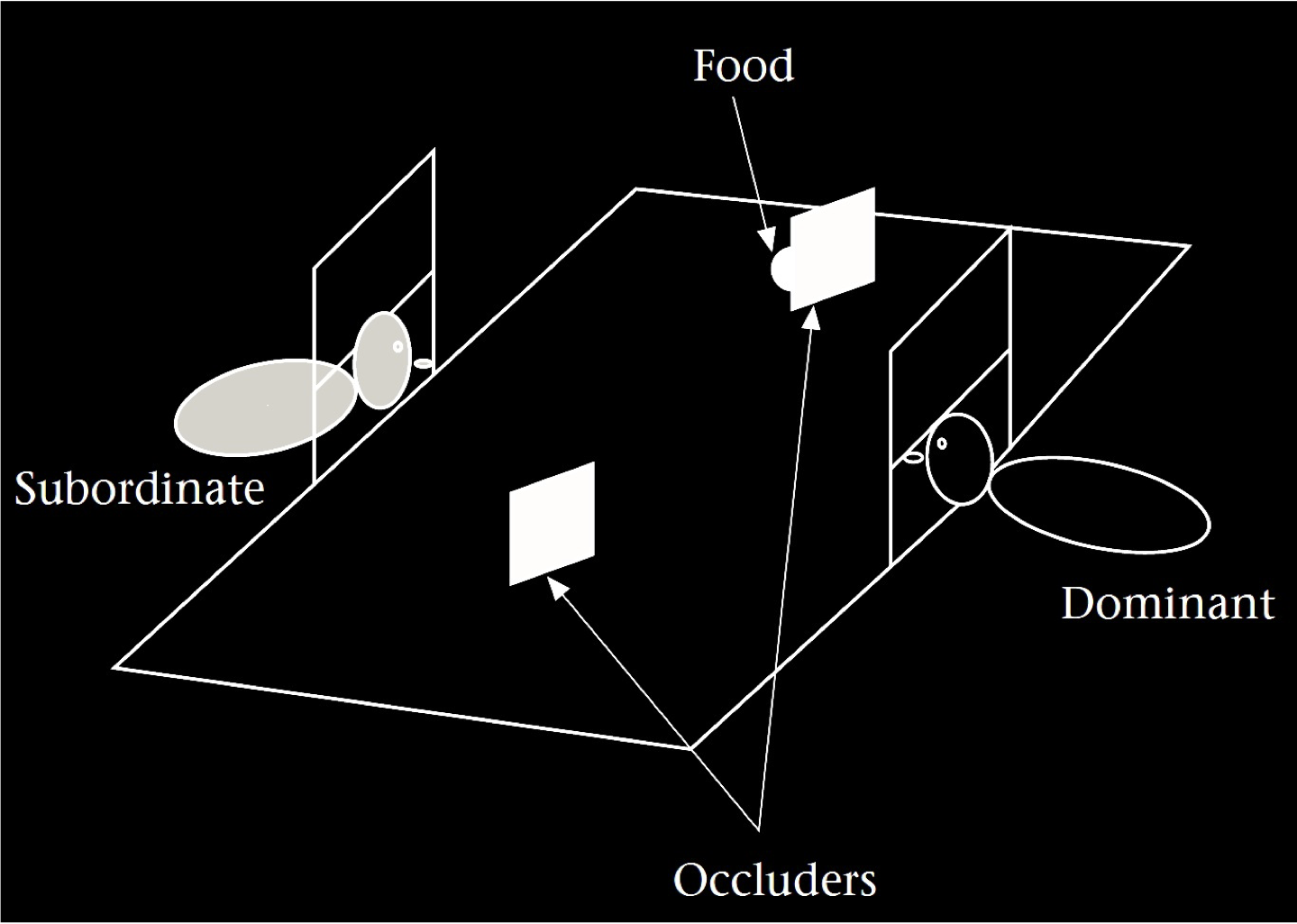
Hare et al (2001, figure 1)
What models of minds and actions, and of behaviours,
and what kinds of processes,
underpin mental state tracking in different animals?
Way forward:
1. Construct a theory of behaviour reading
2. Construct a theory of mindreading

conclusion
1. There is a better* question to ask about nonhuman mindreading.
2. The conjecture that minimal theory of mind characterises a nonhuman’s model of minds and actions can be tested using signature limits.
3. The Teleological Stance provides a computational description of pure goal tracking.
(And so provides a first step towards a theory of behaviour reading.)
4. Mindreading in humans is sometimes but not always automatic.

Radical Interpretation Reprise
The domain: what is a theory of social cognition a theory of?
Social cognition:
cognition of
others’ actions and mental states
in relation to social functioning.
The question: Radical Interpretation*
How in principle could someone infer facts about actions and mental states from non-mental evidence?
What is the relation between an account of radical interpretation* and a theory of social cognition?
A theory of radical interpretation* is supposed to provide a computational description of social cognition.
radical interpretation*
Infer The Mind from The
The Mind: facts about actions, desires, beliefs, emotions, perspectives ...
The Evidence: facts about events and states of affairs that could be known without knowing what any particular individual believes, desires, intends, ...
Theories of radical interpretation*:
The Intentional Stance (Dennett)
Davidson’s Theory
The Teleological Stance & Your-Goal-Is-My-Goal
Minimal Theory of Mind
also an implicit theory associated with perception of emotion
‘the intentional stance ...
‘first you decide to treat the object whose behavior is to be predicted as a rational agent;
‘then you figure out what beliefs that agent ought to have , given its place in the world and its purpose.
‘Then you figure out what desires it ought to have, on the same considerations,
‘and finally you predict that this rational agent will act to further its goals in the light of its beliefs’
Dennett (1987, 17)
1. computational description
-- What is the thing for and how does it achieve this?
2. representations and algorithms
-- How are the inputs and outputs represented, and how is the transformation accomplished?
3. hardware implementation
-- How are the representations and algorithms physically realised?
Marr (1992, 22ff)
The Intentional Stance
can be (mis)interpreted as an attempt to provide
a computational description of social cognition.
‘the intentional stance ...
‘first you decide to treat the object whose behavior is to be predicted as a rational agent;
‘then you figure out what beliefs that agent ought to have , given its place in the world and its purpose.
‘Then you figure out what desires it ought to have, on the same considerations,
‘and finally you predict that this rational agent will act to further its goals in the light of its beliefs’
Dennett (1987, 17)
1. Humans can distinguish each others desires in ways unrelated to their purpose and place in the world.
BUT
2. The Intentional Stance provides no way to do this.
3. The Intentional Stance does not provide a correct computational description of human social cognition.
Objection 1
The Intentional Stance provides
no way to identify
false beliefs, ‘incorrect’ desires or failures of rationality.
Objection 2
The Intentional Stance provides
no adequate way to
distinguish me from you.
1. Humans can sometimes identify false beliefs, ‘incorrect’ desires or failures of rationality.
BUT
2. The Intentional Stance provides no way to do this.
3. The Intentional Stance does not provide a correct computational description of human social cognition.
Objection 1
The Intentional Stance provides
no way to identify
false beliefs, ‘incorrect’ desires or failures of rationality.
Objection 2
The Intentional Stance provides
no adequate way to
distinguish me from you.
Theories of radical interpretation*:
The Intentional Stance (Dennett)
Davidson’s Theory
The Teleological Stance & Your-Goal-Is-My-Goal
Minimal Theory of Mind
also an implicit theory associated with perception of emotion
‘an action can be explained by a goal state if, and only if, it is seen as the most justifiable action towards that goal state that is available within the constraints of reality’
Csibra & Gergely (1998, 255)
1. action a is directed to some goal;
2. actions of a’s type are normally means of realising outcomes of G’s type;
3. no available alternative action is a significantly better* means of realising outcome G;
4. the occurrence of outcome G is desirable;
5. there is no other outcome, G′, the occurrence of which would be at least comparably desirable and where (2) and (3) both hold of G′ and a
Therefore:
6. G is a goal to which action a is directed.
Objection 1
The Intentional Stance provides
no way to identify
false beliefs, ‘incorrect’ desires or failures of rationality.
Objection 2
The Intentional Stance provides
no adequate way to
distinguish me from you.
1. Humans can sometimes identify false beliefs, ‘incorrect’ desires or failures of rationality.
BUT
2. The Teleological Stance provides no way to do this.
3. The Teleological Stance does not provide a correct computational description of human social cognition.
Dennett, Davidson:
We need a single theory covering all social cognition.
A better approach:
Social cognition involves a cluster of disparate abilities.
These include pure goal ascription.
There is no such thing as a theory of social cognition.
Instead we need a theory for each disparate ability.
Theories of radical interpretation*:
The Intentional Stance (Dennett)
Davidson’s Theory
The Teleological Stance & Your-Goal-Is-My-Goal
Minimal Theory of Mind
also an implicit theory associated with perception of emotion
What do we perceptually experience of others’ mental states?
Evidence:
Humans have categorical perception of expressions of emotion.
Question:
Are expressions of emotion facial configurations?
Observation:
Facial configurations are not diagnostic of emotions (Aviezer et al)
Theory:
The objects of categorical perception are actions directed to the goals of expressing particular emotions (Butterfill, 2015).
Categorical perception of expressions of emotions
| level | specification |
| computational description | The Teleological Stance |
| representations and algorithms | ... are broadly perceptual |
Theories of radical interpretation*:
The Intentional Stance (Dennett)
Davidson’s Theory
The Teleological Stance & Your-Goal-Is-My-Goal
Minimal Theory of Mind
also an implicit theory associated with perception of emotion

Objection 1
The Intentional Stance provides
no way to identify
false beliefs, ‘incorrect’ desires or failures of rationality.
Objection 2
The Intentional Stance provides
no adequate way to
distinguish me from you.
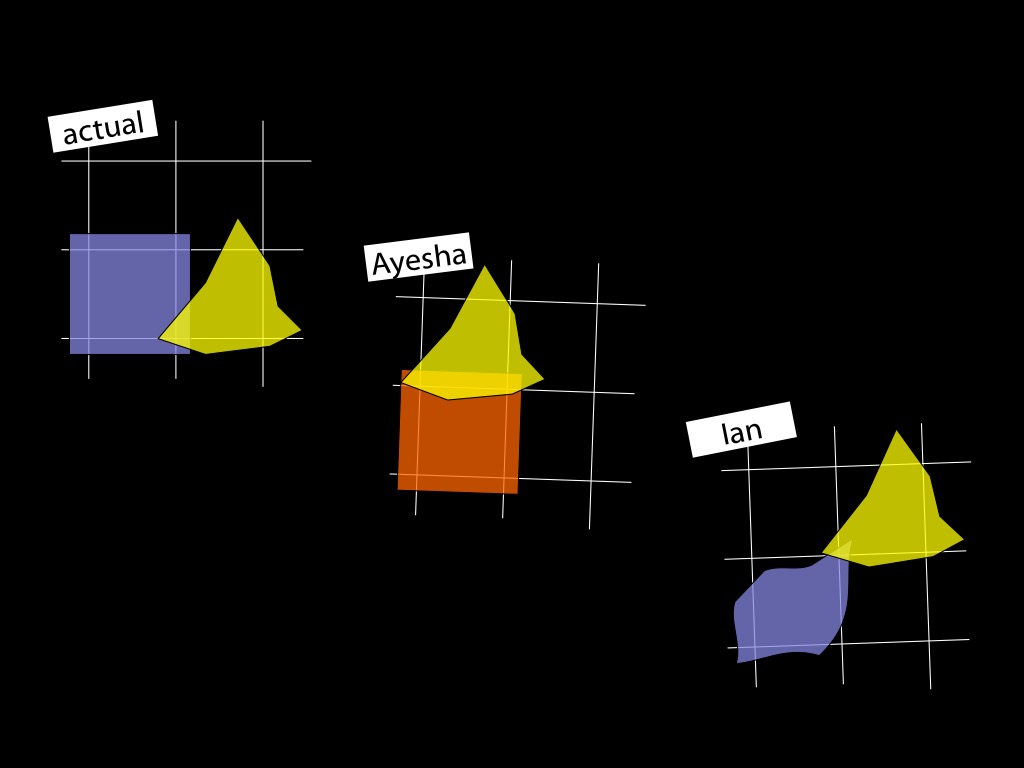
1. Humans can sometimes identify false beliefs involving mistakes about numerical identity.
BUT
2. Minimal Theory of Mind provides no way to do this.
3. Minimal Theory of Mind does not provide a correct computational description of human social cognition.
dogma
the first
of mindreading
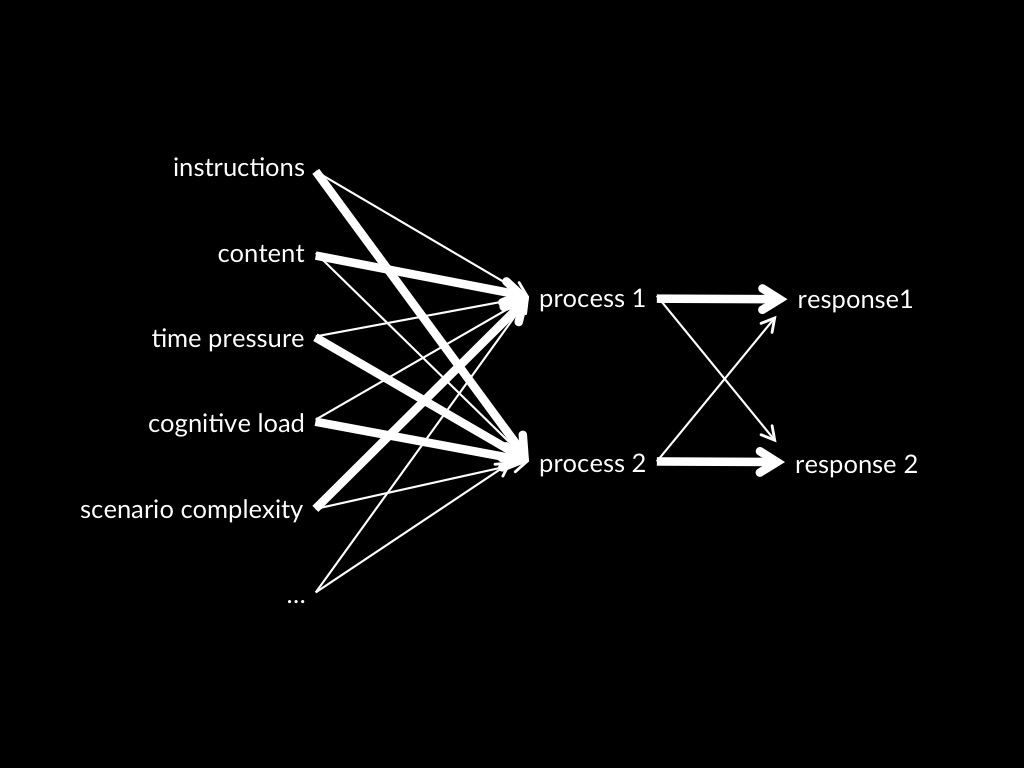
Dual Process Theory of Mindreading (core part)
Two (or more) mindreading processes are distinct:
the conditions which influence whether they occur,
and which outputs they generate,
do not completely overlap.
dogma
the first
of mindreading
Theories of radical interpretation*:
The Intentional Stance (Dennett)
Davidson’s Theory
The Teleological Stance & Your-Goal-Is-My-Goal
Minimal Theory of Mind
also an implicit theory associated with perception of emotion
The domain: what is a theory of social cognition a theory of?
Social cognition:
cognition of
others’ actions and mental states
in relation to social functioning.
The question: Radical Interpretation*
How in principle could someone infer facts about actions and mental states from non-mental evidence?
What is the relation between an account of radical interpretation* and a theory of social cognition?
A theory of radical interpretation* is supposed to provide a computational description of social cognition.